Sagittal imbalance - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
Sagittal alignment involves a harmonious relationship between the cranium, spine, and pelvis. Cervical, Thoracic and Lumbar curves should be proportional in order to maintain a sagittal balance, which occurs when the gravity line, originating from the external auditory canal, runs along the acromion, greater trochanter, lateral knee condyle and lateral malleolus. When alignment of the spine is lost, some compensatory mechanisms are implemented in order to avoid an imbalance. The spinal muscles must counteract this imbalance and thereby fatigue, which often results in severe pain.
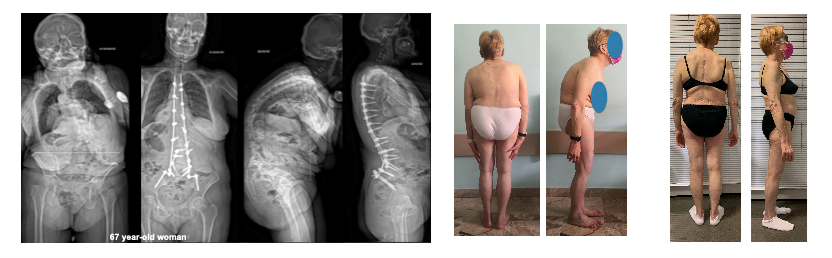
The patient in the pictures presented complaining for severe back pain with gradually progressive anterior trunk flexion.
At the time of presentation, she showed a sagittal imbalance, although many compensatory mechanisms, such as pelvic retroversion and knees flexion, were shown.
The standard radiographs showed a global kyphosis with sagittal imbalance. Surgery was suggested because of the worsening of the deformity and the symptoms that have arisen.
A posterior three-column osteotomy (PSO) that consists in a resection of part of a vertebra was performed.
The technique of posterior correction and fusion consists in the placement of pedicle screws in the vertebrae and pre-shaped rods considering the proper curves of the spine, which allows a restoration of the alignment of the column. Locally harvested autologous bone is placed in order to obtain fusion. After the surgery, a proper balance of the spine was obtained, which reduce the fatigue of the muscles.
Years after the operation, the patient was pain free and the follow-up radiographs demonstrate a good deformity correction and a balanced spine.